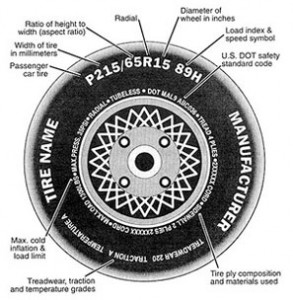
What do all those numbers (and letters) really mean?
Here’s a short primer on tire-related terminology that should help you get to know your four friends a bit better:
* Contact Patch –
As your tires rotate, only a portion of the total tread is actually in contact with the ground at any given moment. This is known as the contact patch. Think of it as your tire’s “footprint.” Sport/performance-type tires are characterized by their wider footprint – more tread is in contact with the ground – which provides extra grip, especially during hard acceleration on dry pavement and during high-speed cornering.
* Treadwear indicators –
These are narrow bands built into the tread during manufacturing that begin to show when only 1/16 of the tire’s tread remains. Also called wear bars, treadware indicators are there to provide an obvious visual warning that it’s time to shop for new tires.
* Speed ratings –
An alpha-numeric symbol you’ll find on your tire’s sidewall that tells you the maximum sustained speed the tire is capable of safely handling. An H-rated tire, for example, is built to be safe for continuous operation at speeds up to 130 mph. Most current model year family-type cars have S (112 mph) or T (118 mph) speed ratings. High-performance cars often have tires with a V (149 mph) or ZR (in excess of 149 mph) speed rating. A few ultra-performance cars have W (168 mph) and even Y (186 mph) speed-rated tires. High-speed tires usually also provide better braking and handling performance, although they tend to wear faster, too, because of their softer tread compounds.
* Maximum cold inflation load limit –
This refers to the maximum load that can be carried in a given vehicle with a given type of tires – and the maximum air pressure needed to support that load. In your vehicle’s owner’s manual, you should be able to find the recommended cold inflation load limit. It’s important not to exceed the load limit (or over or under-inflate the tires) as this can lead to stability/handling problems and even tire failure. Always check tire pressure “cold.” Driving creates friction which creates heat; as the tires warm up, the air inside expands, increasing the pressure. Measuring air pressure after driving can give a false reading; you may actually be driving around on under-inflated tires.
* Load index –
This number corresponds to the load carrying capacity of the tire. The higher the number, the higher the load it can safely handle. As an example, a tire with a load index of 89 can safely handle 1,279 pounds – while a tire with a load rating of 100 can safely handle as much as 1,764 pounds. It’s important to stick with tires that have at least the same load rating as the tires that came originally with the vehicle – especially if it’s a truck used to haul heavy loads or pull a trailer. It’s ok to go with a tire that has a higher load rating than the original tires; just be careful to avoid tires with a lower load rating than specified for your vehicle, even if they are less expensive. Saving a few bucks on tires is not worth risking an accident caused by tire failure.
* Aspect ratio –
This technical-sounding term refers to the relationship between the width of a tire and the height of the tire’s sidewall. High-performance “low profile” tires have “low aspect ratios” – meaning their sidewalls are short relative to their width. This design provides extra stiffness and thus better high-speed handling and grip – but also tends to result in a firmer (and sometimes, harsh) ride. “Taller” tires, on the other hand, tend to provide a smoother ride and better traction in snow.
* Radial vs. bias-ply tire –
Bias-ply tires have their underlying plies laid at alternate angles less than 90 degrees to the centerline of the tread; radials have their plies laid at 90 degrees to the centerline of the tread. That’s the technical difference. The reason radial tires are dominant today is that they help improve fuel efficiency and handling; they also tend to dissipate heat better than bias-ply tires. No modern passenger cars come with bias-ply tires and their use is generally not recommended. (Exception might include older/antique vehicles that originally came equipped with bias-ply tires. Some RVs also used bias-ply tires, etc.) It is very important never to mix radial and bias-ply tires; dangerously erratic handling may result.
* LT and MS tires –
These designations indicate “Light Truck” and “Mud/Snow” – and are commonly found on tires fitted to 4WD SUVs and pick-ups. LT-rated tires are more general purpose, built primarily for on-road use – while MS-rated tires typically have more aggressive “knobby” tread patterns designed for better off-road traction.
* Temporary Use Only –
Many modern cars come with “space-saver” tires which are smaller and lighter than a standard or full-size spare tire. They are designed to leave more room in the trunk and be easier for the average person to handle when a roadside tire change becomes necessary. However, they are for temporary use only – and not designed to be used for extended periods (or high-speed) driving. Your car will probably not handle (or stop) as well while the space saver tire is on; to be safe, you should keep your speed under 55 mph and avoid driving on the tire beyond what’s absolutely necessary to find a repair shop where you can have your damaged tire repaired or replaced.
* Treadwear, Traction and Temperature ratings –
Each tire has three separate ratings for Treadwear, Traction and Temperature. Traction ratings run from AA to A to B and C – with C being the lowest on the scale. The ratings represent the tire’s ability to stop on wet pavement under controlled testing conducted by the government. C-rated tires are marginal and should be avoided. Never buy a tire with a Traction rating that isn’t at least equal to the minimum rating specified by the manufacturer of your vehicle.
Temperature ratings from A to B to C – with C being the minimum allowable for any passenger car tire. The ratings correspond to a given tire’s ability to dissipate heat under load; tires with lower ratings are more prone to heat-induced failure, especially if driven at high speeds (or when overloaded). As with Traction ratings, never buy a tire with a Temperature rating that’s less than specified for your vehicle.
Treadwear ratings differ from Traction and Temperature ratinsg in that they aren’t a measure of a tire’s built-in safety margin. Instead, these ratings – represented by a three digit number – give you an idea of the expected useful life of the tire according to government testing. A tire with a Treadwear rating of 150, for example, can be expected to last about 1.5 times as long as a tire with a Treadwear rating of 100. These are just guides, however. Your tires may last longer (or not) depending on such factors as how you drive, whether you maintain proper inflation pressure and rotate the tires per the recommendations – and so on.










And
Tire Manufacture Date – The Production Code
The production code on all tires are not equal but you will see a special code in an ellipse shape on at least 80% of all tires on the market, and that will help you find tire date of manufacture.
The “last 4 digits” on the ellipse tells us tire manufacture date. The first 2 digits is “PRODUCTION WEEK” and the last 2 digits is the “YEAR”. Assuming there are 4 weeks in a month, we can say that this tire was manufactured by the end of March 2003 (12=12th week of the year, 03=Year 2003).
5000 means 50th week of year 2000, which means December 2000.